ABOUT Strategic Air Command
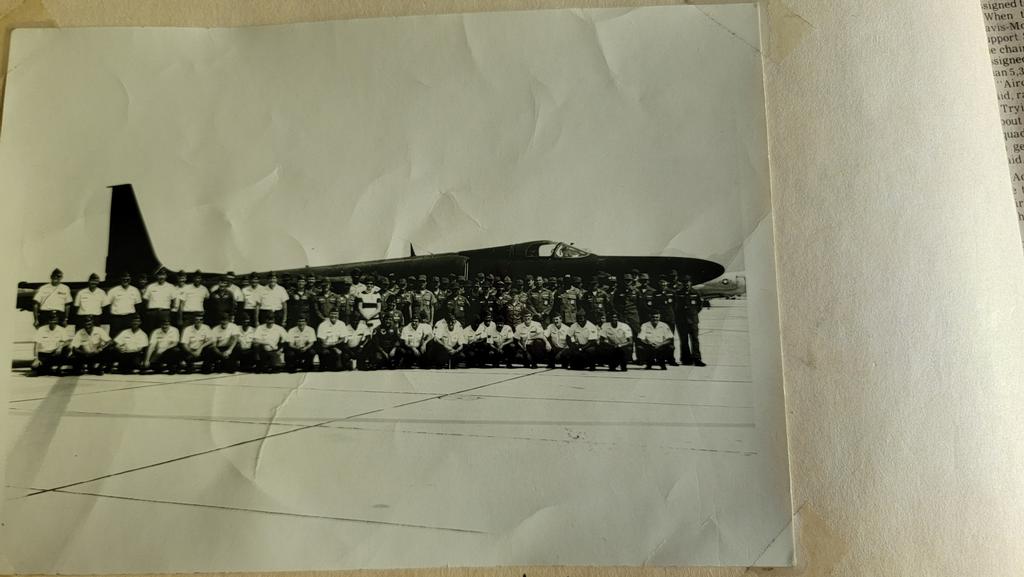
- The Strategic Air Command (SAC) was established on March 21, 1946, as a branch of the United States Army Air Forces.
- SAC was responsible for the strategic nuclear weapons delivery of the United States during the Cold War.
- During the height of the Cold War, SAC maintained a fleet of B-52 Stratofortress bombers on 24-hour airborne alert to ensure a swift response to any potential nuclear threat.
- General Curtis LeMay was one of the most influential leaders of SAC, serving as its commander from 1948 to 1957.
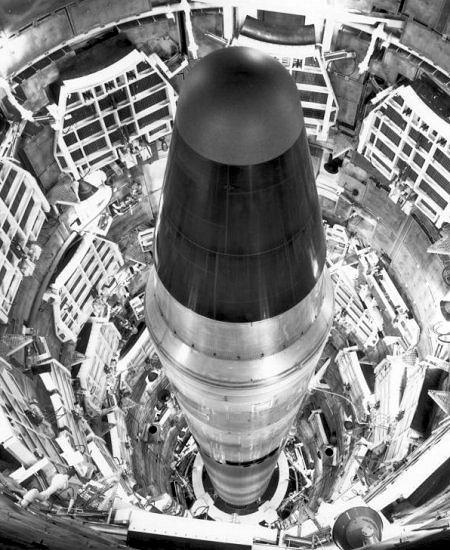
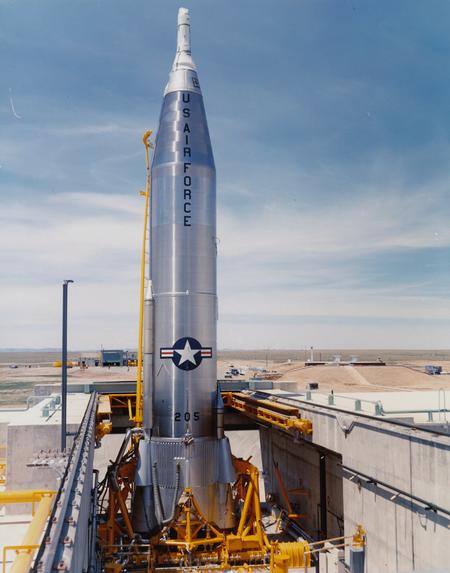
- SAC also played a key role in the development and deployment of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) during the 1950s and 1960s.
- In 1966, SAC suffered a major setback when a B-52 carrying four hydrogen bombs crashed in Greenland, leading to the contamination of the area with radioactive material.
- SAC was disbanded in 1992 following the end of the Cold War, and its responsibilities were transferred to the newly established United States Strategic Command.
- During its existence, SAC played a crucial role in deterring the Soviet Union and maintaining the balance of power during the Cold War.
- SAC's motto was "Peace is Our Profession," reflecting its mission to prevent war through the threat of overwhelming force.
- The legacy of SAC continues to influence the United States' nuclear strategy and defense policy to this day.